Infor LN & Baan Tips & Tricks for EXECUTIVES
TECHNOLOGY: Using the Data Access Layer (DAL)
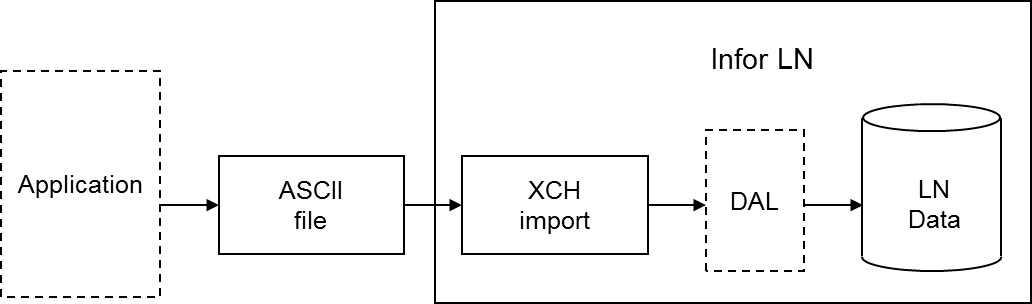
During an Exchange import, you can use all the functionality programmed into the Data Access Layer (DAL). If you use the DAL, Exchange carries out all the constraint checks, integrity checks, and side effects, for example, updates on other tables, that are programmed into the DAL. Database integrity is guaranteed automatically.
Using the DAL reduces the costs of interface development. You can use the DAL to import standard interfaces developed by Infor for partner products, as well as for specific interfaces built by customers, for example, to integrate LN with legacy systems. You can use the DAL in both single site and multisite environments.
The checks or additional actions specified in the DAL are carried out for each row that is imported. Database errors are logged in the same way for DAL and non-DAL import. DAL hook errors are also logged. You can specify whether the DAL property checks are or are not carried out.
If you specify the use of the DAL for a table relation for an import, the dal.new, dal.update, and dal.destroy functions are used instead of db.insert, db.update, and db.delete. You can choose to use DAL for particular tables and not for other tables, therefore, an import batch can contain both types of table relations simultaneously. The import through DAL works for both the import based on audit or indicators (inserts, updates, deletes), and the full import (inserts only).
DAL settings are run time aspects, which means you can change these aspects without having to regenerate the import program. DAL settings are also logged in the log table at batch line level, to enable you to find out what the DAL settings were when the import was run.
Important to realize is that an update through the DAL can result in a number of side effects. Actions performed by the DAL must not be carried out twice. For example, if the DAL updates the available to promise (ATP) quantity for an item when importing order data, the ATP quantity must not be updated in a condition script as well.
For this reason, you must not add any actions in condition scripts, or import additional data, that are already handled in the DAL.
FINANCE: Set Up and Calculate Currency Differences
To set up and calculate currency differences for foreign currencies:
- Use the Company Parameters (tfgld0503m000) session to specify the profit and loss ledger accounts, 12 profit and loss dimensions, and transaction type for a posting exchange rate differences that is calculated using the FIFO method. To specify this data, use the Currency Diff. FIFO tab. The reports printed from the Print Company Parameters (tfgld0404m000) session, include the Currency Differences FIFO fields.
- Use the Calculate Currency Differences (tfgld5201m000) session to calculate the currency differences resulting from transactions posted on accounts for which the field Currency Analysis in the session Chart of Accounts (tfgld0508m000) is set to Required.
OPERATIONS: Subcontracting Overview
Companies can decide to involve a subcontractor and subcontract part of their activities. The subcontractor carries out the work and returns the products to your company.
In Infor LN, subcontracting is considered as purchasing labor from a third party. Therefore, if a manufacturer wants to subcontract work, he must generate a purchase order to start the subcontracting process. These are the types of subcontracting:
- Subcontracting with material flow
- Operation subcontracting: For operation subcontracting, a part of the production process (one or more operations) is subcontracted.
- Item subcontracting: For item subcontracting, an item's entire production process is subcontracted. Therefore, it is always used with material flow support.
- Subcontracting without material flow: The simplest form of subcontracting is to generate a subcontracting purchase order to record the operations outsourced to a subcontractor. The subcontracting purchase order only represents the administrative handling of the subcontracting process. When the subcontracted item is received back from the subcontractor, you must close the subcontracting purchase order, which initiates the production process.
- Unplanned subcontracting: Unplanned subcontracting is applicable when you subcontract after generating a production order. For unplanned subcontracting, a purchase order is generated from the production order and the material supply lines are populated by Shop Floor Control.
- Service subcontracting: For service subcontracting, work on an item to be maintained or repaired is subcontracted. This work entails the entire repair process, or only a part of it. Service subcontracting can be used with or without material flow support.
To start the subcontracting process, a purchase order is required.